Taxodium distichum
Photographs belong to the photographers who allow use for FNPS purposes only. Please contact the photographer for all other uses.
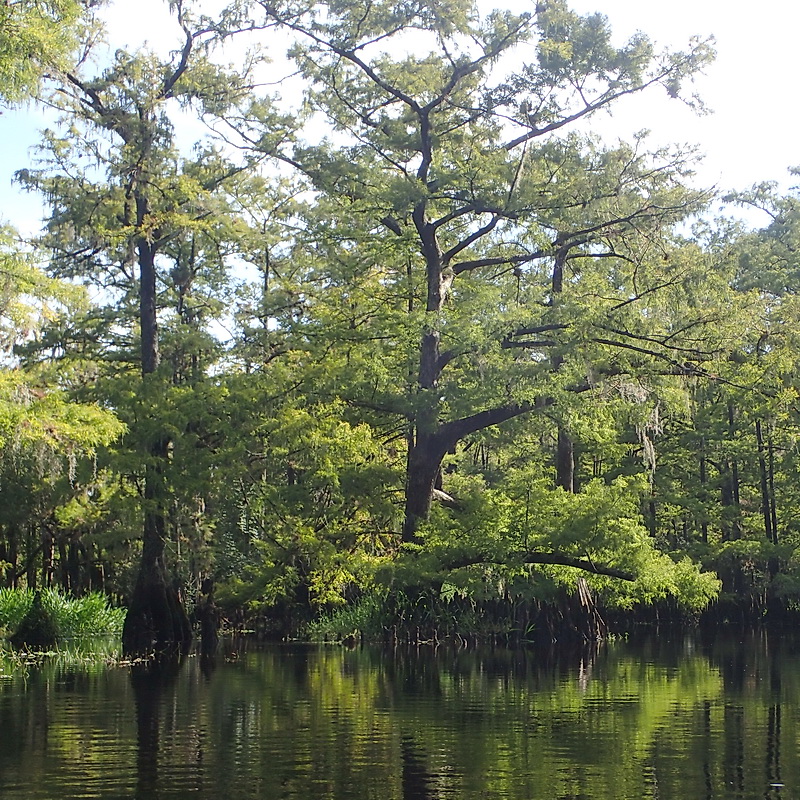
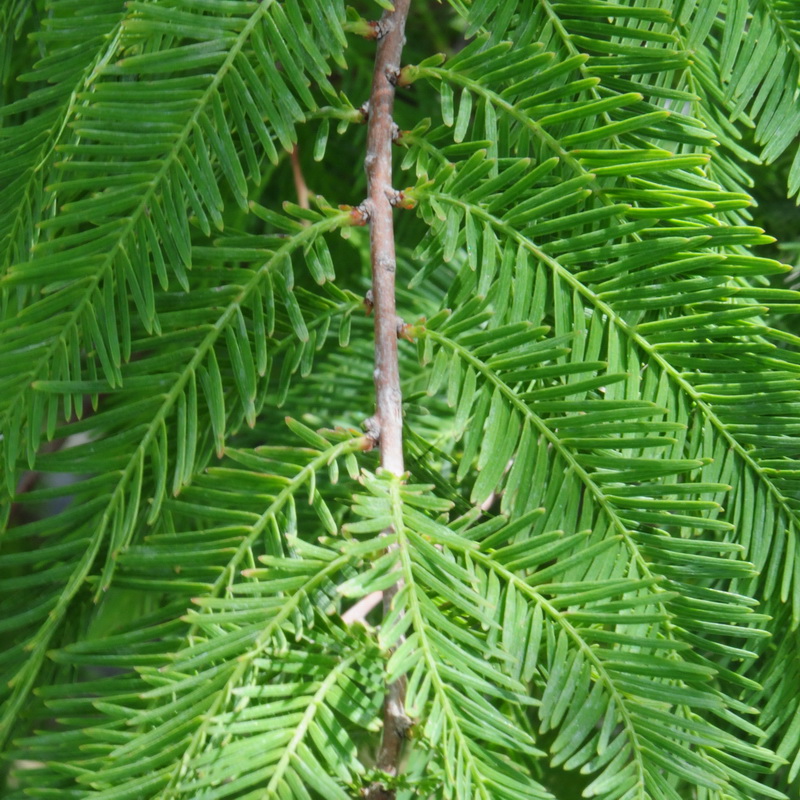
Bald Cypress
Cupressaceae
Plant Specifics
| Form: | Tree | |
| Size: | 50 - 75 ft tall by 30-45 ft wide | |
| Life Span: | Long-lived perennial | |
| Flower Color: | NA | |
| Fruit Color: | Brown | |
| Phenology: | Deciduous. Very long-lived possibly exceeding 1000 yrs (Nelson 2003). | |
| Noted for: | Fall color, Interesting foliage, Hurricane wind resistance |
Landscaping
| Recommended Uses: | Can be used as a specimen tree, planted in floodplain areas, or planted in relatively moist uplands. Large rain gardens and bioswales. Tolerant of root disturbance, so a candidate for use as a street/parking lot tree. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Considerations: | Can produce knees, even if grown in uplands. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propagation: | Can be grown from seed. Requires moist but not inundated sites for germination and early growth. Requires flooding for seed dispersal. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Availability: | Native nurseries, FNPS plant sales, Quality nurseries, Seed, Specialty providers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Light: | Full Sun, Part Shade | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Moisture Tolerance: |
always floodedextremely dry |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Stays Wet ----- to ----- Somewhat moist, no flooding) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Moisture Tolerance: | Stays Wet ----- to ----- Somewhat moist, no flooding | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salt Water Flooding Tolerance: | Not salt tolerant of inundation by salty or brackish water. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salt Spray/ Salty Soil Tolerance: | Low/no tolerance of salty wind or direct salt spray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Soil or other substrate: | Pond, lake, or stream bottom, Clay, Loam, Organic material (muck), Sand | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Soil pH: | Acidic to neutral | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ecology
| Wildlife: |
Attracts seed-eating birds. Valuable as roosting and nesting areas for colonial wading birds. | |
| Insects: | Larval host for baldcypress sphinx (Isoparce cupressi) moth. | |
| Native Habitats: | Riverine swamps, large swamps around lakes. Inundated areas associated with some form of flowing water. Floodplains, sloughs, strands. May be associated with a longer fire return interval than T. ascendens. |
Distribution and Planting Zones
Natural Range in Florida
USDA Zones
Suitable to grow in:
10A 10B 8A 8B 9A 9B
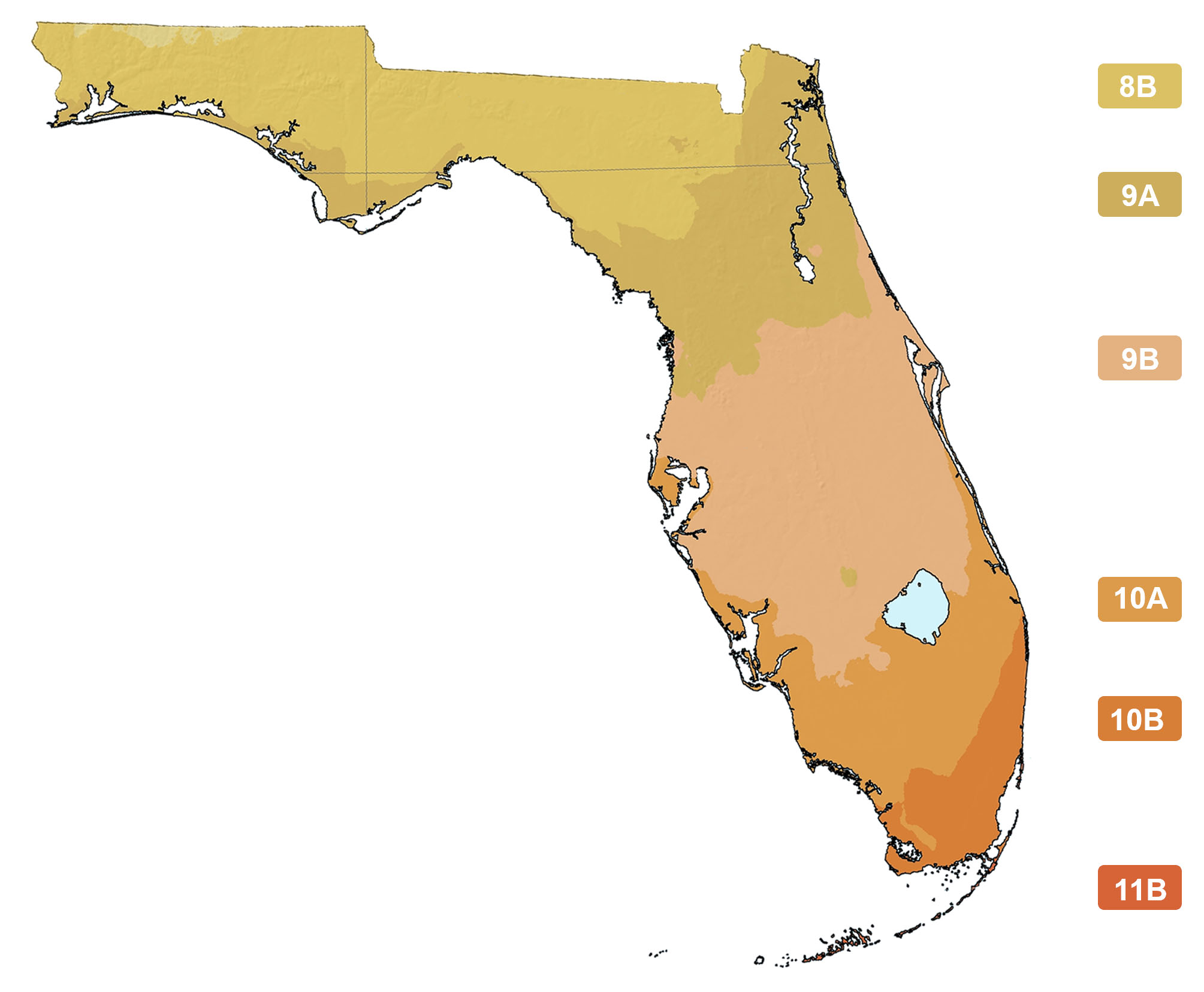
USDA zones are based on minimum winter temperatures
Comments
| Ethnobotany: | Old trees were exceeding valuable as a source of wood that was rot resistant. Younger trees with little heartwood do not share this characteristic. | |
| General Comments: | Younger specimens have a conical shape, but older trees tend to flatten out at the top. In some areas, the strangler fig (Ficus aurea)has strangled many mature bald cypress trees--The Corkscrew Swamp is an example of this. |




