Comunidades de plantas nativas de Florida
Acidic, Low Nutrient Lake
Las fotografías pertenecen a los fotógrafos que permiten su uso únicamente para fines de FNPS.
Información
Variantes de la comunidad:
Sandhill Upland Lake, Coastal Dune Lake
Descripción:
Upland lakes are typically found in sandy uplands, receiving most of their water from surface runoff and seepage from the surficial aquifer. They are not generally connected to stream systems and are not spring-fed from the limestone aquifer.
The water is usually clear, and the substrate is generally sandy. Vegetation is sparse and mostly restricted to shallow margins.
These lakes can lose their oligotrophic character if the surrounding watershed is heavily fertilized, used for animal husbandry, or developed. In such cases, nutrient enrichment can lead to eutrophication, shifting the community type. Research has also shown that upland lakes can be acidified by atmospheric deposition (acid rain). For example, at Lake Annie in Highlands Hammock, pH dropped from above 6.0 to about 5.1 between 1966 and 1992, a rapid decline triggered when the watershed’s buffering capacity was depleted (Battoe & Lowe, 1992).
Variants
Sandhill Upland Lakes: Found in “sandhill” or high pine settings, typically within old sinkholes. They show high water-level fluctuations. Good examples occur at Mike Roess Gold Head Branch State Park.
Coastal Dune Lakes: Found near the Gulf Coast, these are freshwater (sometimes slightly brackish) systems with clear, tannic (tea-colored) water. Some periodically connect to the Gulf during overflow events, and saltwater may intrude during storm surges. Good examples occur at Topsail Hill State Park and Deer Lake State Park.
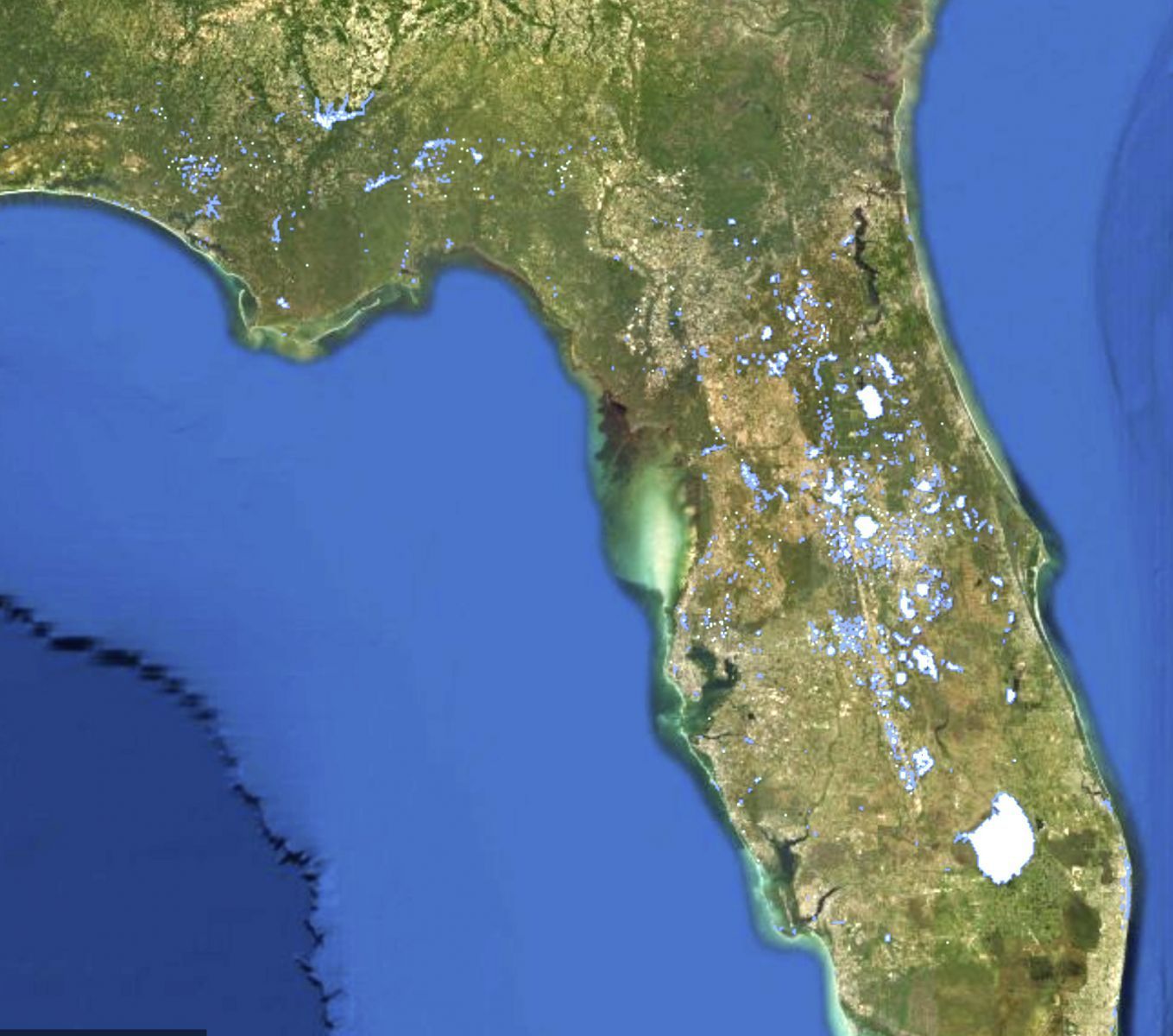
Map of Florida Lakes, from Florida Lake Watch website with the map restricted to showing lakes and ponds only. This map does not classify lakes by pH or trophic state.
Referencias:
Battoe, L. E., & Lowe, E. F. (1992). Acidification of Lake Annie, Highlands Co., FL. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 65, 69–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00477098
Florida Natural Areas Inventory. (2010). Guide to the natural communities of Florida: 2010 edition. Florida Natural Areas Inventory. http://fnai.org/naturalcommguide.cfm
Hoyer, M., Canfield, D. E., Jr., Horsburgh, C. A., & Brown, K. (1996). Florida freshwater plants: A handbook of common aquatic plants in Florida lakes. University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences.
Schiffer, D. M. (1998). Hydrology of central Florida lakes: A primer (U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1137). U.S. Geological Survey. http://fl.water.usgs.gov/PDF_files/c1137_schiffer.pdf
University of South Florida Water Institute. (2020). Florida atlas of lakes. https://maps.wateratlas.usf.edu/AtlasOfLakes/
Whitney, E. N., Means, D. B., & Rudloe, A. (2004). Priceless Florida: Natural ecosystems and native species. Pineapple Press.
Haga clic para obtener más información sobre las diferentes comunidades de plantas de Florida o desplácese por la página para ver toda la maravillosa diversidad única que se puede explorar.
Tierras altas xéricas (muy secas)
Tierras altas algo secas
Tierras altas húmedas
Tierras rocosas
llanuras húmedas
Humedales de la cuenca
Humedales de filtración
Humedales con aguas de movimiento lento
Humedales de llanura aluvial
Arroyos
Lagos y estanques
Tierras altas costeras
Humedales costeros







