Comunidades de plantas nativas de Florida
Dry Prairie
Las fotografías pertenecen a los fotógrafos que permiten su uso únicamente para fines de FNPS.
Información
Variantes de la comunidad:
N/A
Descripción:
Dry prairie occurs on extensive flat landscapes with sandy soils, usually underlain by a hardpan at moderate depth. Fire is frequent and essential to maintaining this community.
Vegetation is dominated by wiregrass ( Aristida stricta ) and a rich diversity of seasonal wildflowers. Palmettos ( Serenoa repens ) may be present, but their abundance often reflects past grazing and winter burning. True dry prairie was never forested and should not be considered flatwoods without an overstory.
Most of Florida’s dry prairie has been converted to agriculture, but notable remnants can be found at Three Lakes Wildlife Management Area, Kissimmee Prairie State Park, Myakka River State Park, and the Avon Park Air Force Range.
A Walk in the Dry Prairie at Kissimmee Prairie State Park
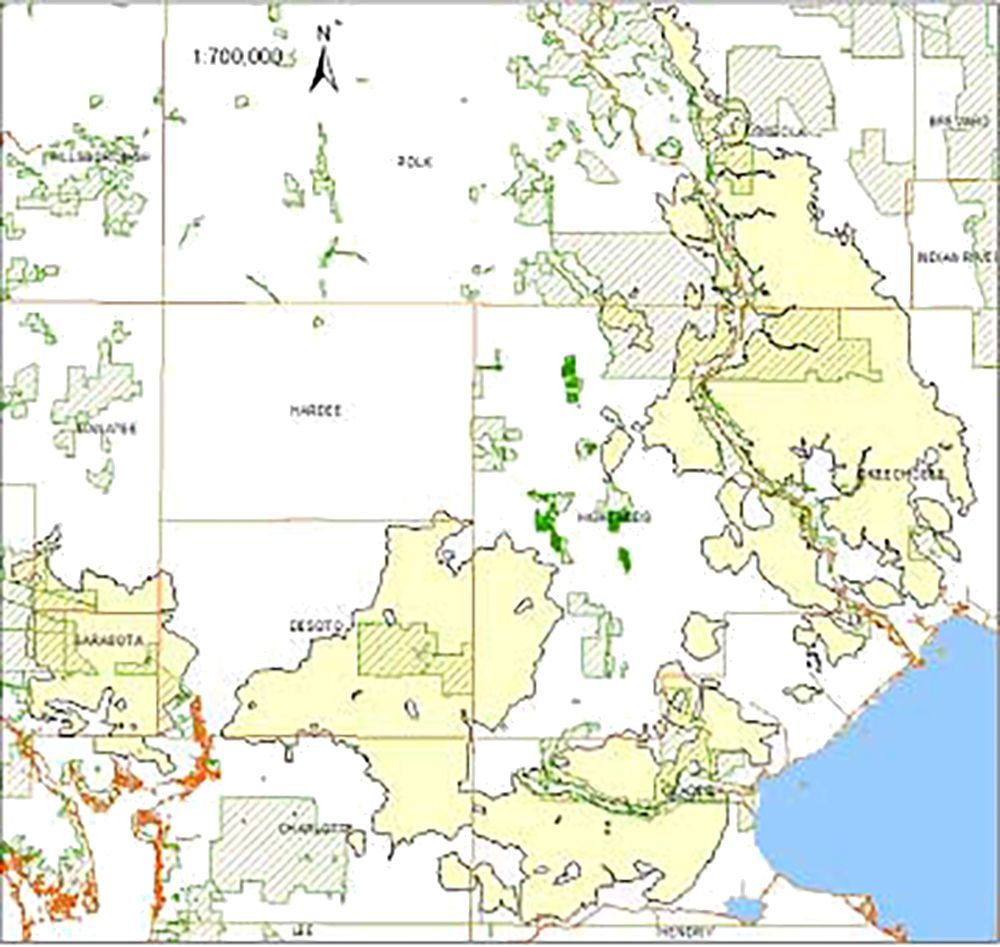
Presettlement extent of dry prairie. Map created by Edwin Bridges. It was prepared from original land surveys conducted mostly between 1820 and 1870 and the areas of prairie include not only the prairie but other, smaller plant communities that would have been embedded within it. Much less remains today. From the program of the Florida Dry Prairie Conference, 2004. http://www.ces.fau.edu/fdpc/dpregion.php.
Referencias:
Florida Department of Environmental Protection. (1992). Soil and water relationships of Florida's ecological communities. http://www.dep.state.fl.us/water/wetlands/delineation/docs/soil-and-water.pdf
Florida Natural Areas Inventory. (2010). Guide to the natural communities of Florida: 2010 edition. Florida Natural Areas Inventory. http://fnai.org/naturalcommguide.cfm
Knight, G. R., Oetting, J. B., & Cross, L. (2011). Atlas of Florida's natural heritage: Biodiversity, landscapes, stewardship and opportunities. Institute of Science and Public Affairs, Florida State University.
Myers, R. L., & Ewel, J. J. (Eds.). (1990). Ecosystems of Florida. University of Central Florida Press.
Noss, R. F. (2013). Forgotten grasslands of the South: Natural history and conservation. Island Press.
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Soil Conservation Service. (1986). 26 ecological communities of Florida. http://ufdc.ufl.edu/UF00000110/00001
Whitney, E. N., Means, D. B., & Rudloe, A. (2004). Priceless Florida: Natural ecosystems and native species. Pineapple Press.
Haga clic para obtener más información sobre las diferentes comunidades de plantas de Florida o desplácese por la página para ver toda la maravillosa diversidad única que se puede explorar.
Tierras altas xéricas (muy secas)
Tierras altas algo secas
Tierras altas húmedas
Tierras rocosas
llanuras húmedas
Humedales de la cuenca
Humedales de filtración
Humedales con aguas de movimiento lento
Humedales de llanura aluvial
Arroyos
Lagos y estanques
Tierras altas costeras
Humedales costeros






