Florida's Native Plant Communities
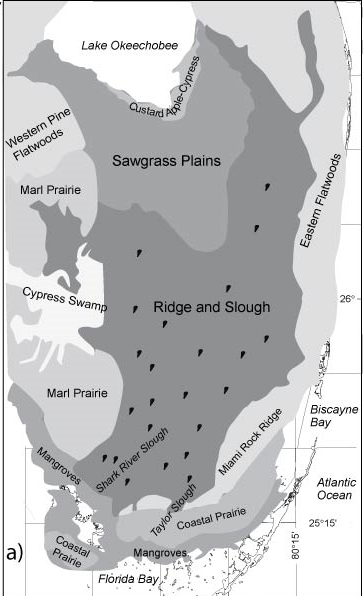
Marl Prairie
Photographs belong to the photographers who allow use for FNPS purposes only.
Information
Community Variants:
Everglades, Wetland Glades
Description:
Marl prairie occurs in subtropical peninsular Florida and is characterized by a marl over limestone substrate. It is seasonally inundated, with a hydroperiod of approximately 2–4 months (FNAI, 2010; Duever et al., 1986). Water movement is slow and often imperceptible, gradually flowing toward the coast and into deeper marshes and sloughs. Fire frequency varies from rare to frequent, though frequent fire is likely the natural norm.
Marl prairies may support over 100 plant species, but the majority of cover usually comes from just a few dominant species, which vary depending on local hydrology. Common dominants include Gulf hairawn muhly ( Muhlenbergia capillaris var. filipes ), spreading beaksedge ( Rhynchospora microcarpa ), Florida little bluestem ( Schizachyrium maritimum ), black bogrush ( Schoenus nigricans ), Elliott’s lovegrass ( Eragrostis elliottii ), sand cordgrass ( Spartina bakeri ), and sawgrass ( Cladium jamaicense ). In the Big Cypress region, marl prairies often include scattered, stunted, “hatracked” pond cypress ( Taxodium ascendens ), a form described by USDA (1986) as “scrub cypress.” For detailed species lists, see FNAI (2010) and Duever et al. (1986).
Rare and Endemic Species
- Few-flowered fingergrass ( Digitaria pauciflora ) – a South Florida endemic known from only two marl prairie sites.
- Meadow jointvetch ( Aeschynomene pratensis )
- Narrow-leaved Carolina scalystem ( Elytraria caroliniensis var. angustifolia )
- Carter’s large-flowered flax ( Linum carteri var. smallii )
The dwarf cypress trees of marl prairies also support epiphytes, including rare species. One of the most iconic photographs of the cowhorn orchid ( Cyrtopodium punctatum ) documented a plant growing on a dwarf cypress stump—now lost.
Good examples of marl prairie can be found in:
- Everglades National Park
- Big Cypress National Preserve
- Fakahatchee Strand Preserve State Park
Source: Wikipedia ( https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marl_prairie )
References:
Duever, M. J., Carlson, J. E., Meeder, J. F., Duever, L. C., Gunderson, L. H., Riopelle, L. A., Alexander, T. R., Myers, R. L., & Spangler, D. P. (1986). The Big Cypress National Preserve (Research Report 8). National Audubon Society.
Florida Natural Areas Inventory. (2010). Guide to the natural communities of Florida: 2010 edition. Florida Natural Areas Inventory. http://fnai.org/naturalcommguide.cfm
(see also Marl Prairie section: https://www.fnai.org/PDF/NC/Marl_Prairie_Final_2010.pdf
)
Gann, G. D., Bradley, K. A., & Woodmansee, S. W. (2009). Floristic inventory of South Florida database. Institute for Regional Conservation. http://regionalconservation.org/ircs/database/database.asp
Gleason, P. (1972). The origin, sedimentation, and stratigraphy of a calcitic mud located in the southern freshwater Everglades (Doctoral dissertation). Pennsylvania State University.
Gunderson, L. H. (1994). Vegetation of the Everglades: Determinants of community composition. In S. M. Davis & J. C. Ogden (Eds.), Everglades: The ecosystem and its restoration (pp. 323–340). St. Lucie Press.
Gunderson, L. H., & Snyder, J. R. (1994). Fire patterns in the southern Everglades. In S. M. Davis & J. C. Ogden (Eds.), Everglades: The ecosystem and its restoration (pp. 291–305). St. Lucie Press.
Knight, G. R., Oetting, J. B., & Cross, L. (2011). Atlas of Florida's natural heritage: Biodiversity, landscapes, stewardship and opportunities. Institute of Science and Public Affairs, Florida State University.
Myers, R. L., & Ewel, J. J. (Eds.). (1990). Ecosystems of Florida. University of Central Florida Press.
Noss, R. F. (2013). Forgotten grasslands of the South: Natural history and conservation. Island Press.
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Soil Conservation Service. (1986). 26 ecological communities of Florida. http://ufdc.ufl.edu/UF00000110/00001
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. (1999). Multi-species recovery plan for South Florida. https://www.fws.gov/verobeach/MSRPPDFs/HydricPineFlat.pdf
Whitney, E. N., Means, D. B., & Rudloe, A. (2004). Priceless Florida: Natural ecosystems and native species. Pineapple Press.
Wikipedia. (n.d.). Marl prairie. In Wikipedia. Retrieved [today’s date], from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marl_prairie
Click to learn about different Florida plant communities or scroll through the page to see all the wonderful unique diversity to be explored.







